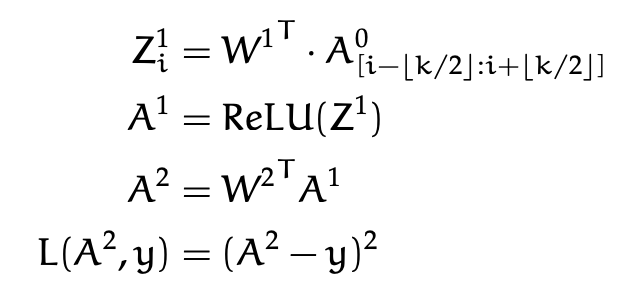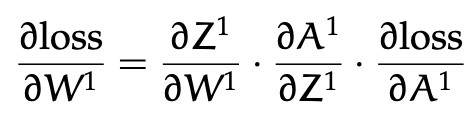Convolutional Neural Networks
PSTAT197A/CMPSC190DD Fall 2024
Final group assignment
Sign up in a Group (3-5 members). [here]
task: create a method vignette on a data science topic or theme
goal: create a reference that you or someone else might use as a starting point next term
deliverable: public repository in the
Capstone-24-25workspace
Possible vignette topics
clustering methods
neural net architecture(s) for … [images, text, time series, spatial data]
analysis of network data
numerical optimization
bootstrapping
geospatial data structures
anomaly detection
functional regression
Outputs
Your repository should contain:
- A brief .README summarizing repo content and listing the best references on your topic for a user to consult after reviewing your vignette if they wish to learn more
- A primary vignette document that explains methods and walks through implementation line-by-line (similar to an in-class or lab activity)
- At least one example dataset
- A script containing commented codes appearing in the vignette
Timeline
Thursday 11/21: No formal lecture - time to prepare final project
let us know your topic by the end of day Monday 11/25
No class on Tuesday 11/26
present a draft in class Tuesday 12/3 and Thursday 12/5
finalize repository by Friday 12/13
Expectations
You’ll need to yourself learn about the topic and implementation by finding reference materials and code examples.
It is okay to borrow closely from other vignettes in creating your own, but you should:
cite them
use different data
do something new
It is not okay to make a collage of reference materials by copying verbatim, or simply rewrite an existing vignette.
- the best safeguard against this is to find your own data so you’re forced to translate codes/steps to apply in your particular case
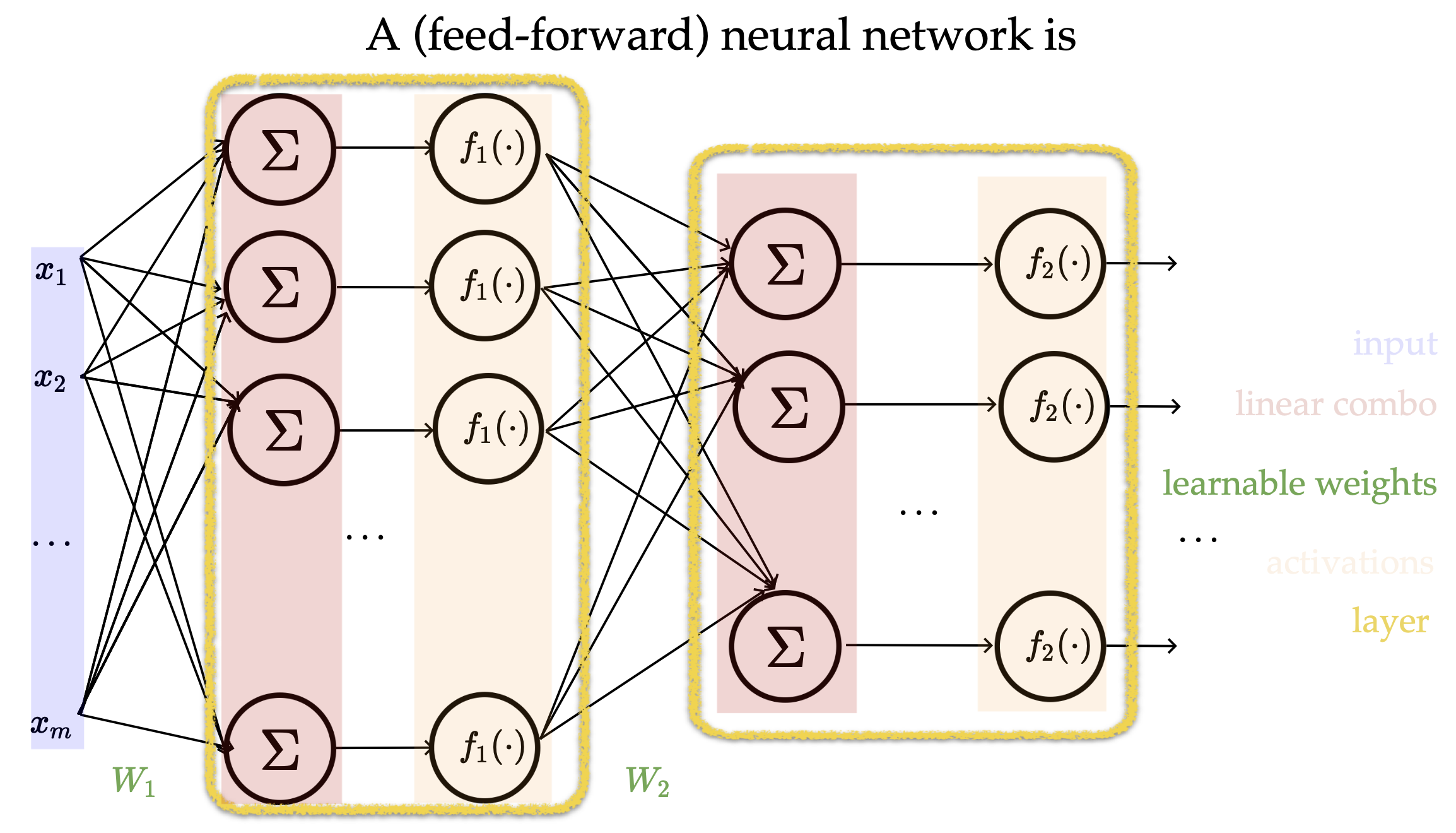
Neural Networks Recap
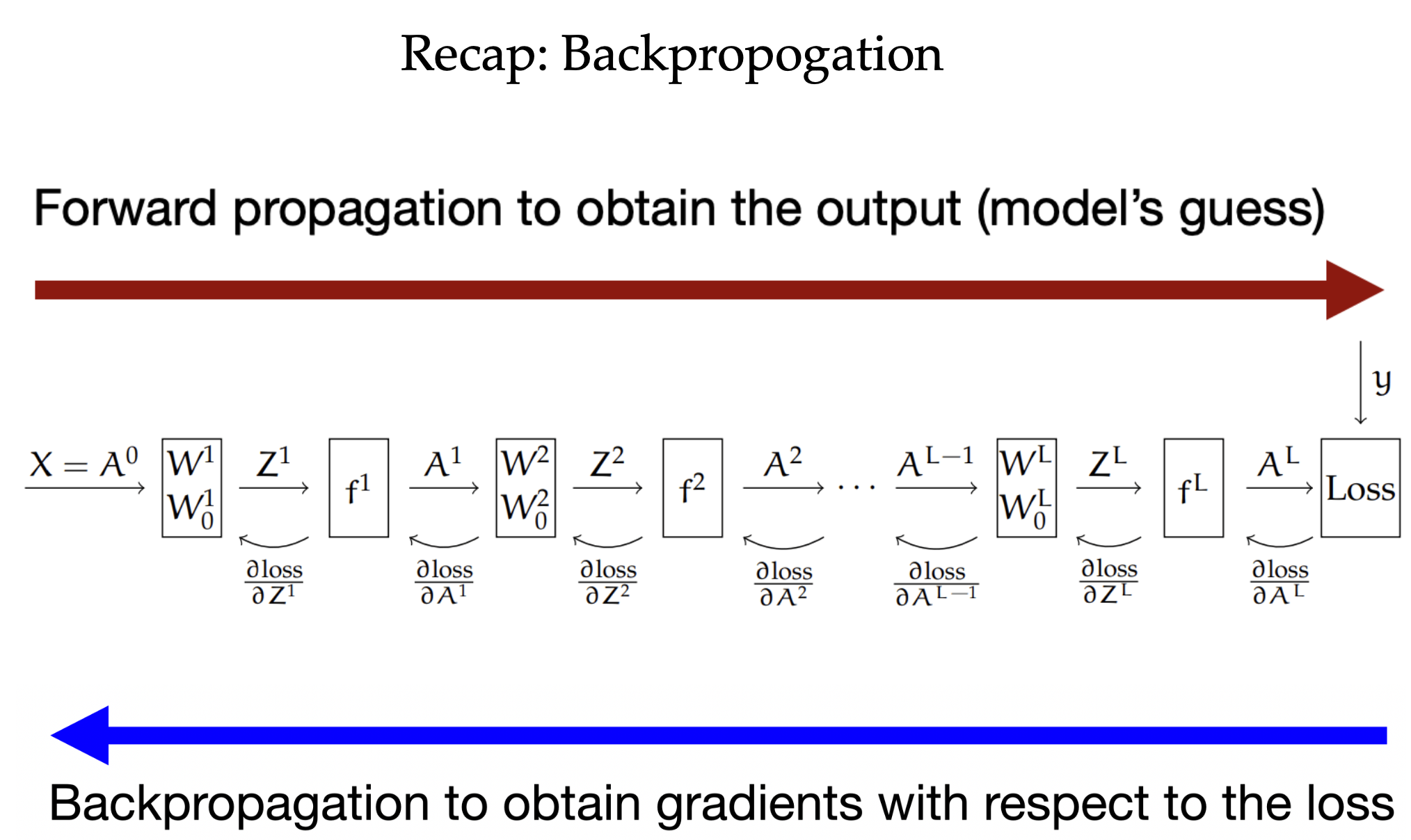
Recap: Backpropagation
Why CNN?
Why CNN?
- Fully-connected nets don’t scale well to (interesting) images. Imagine an image 426 x 426 with a single layer (output size = # of classes, i.e. classes):
- Parameters = 426 x 426 x 10 = 1.9 million
- Image as a signal with spatial dependency:
- Image: Two dimensional signal - set of values related to one another in systematic way (Stochastic process).
- Other examples of signals: Speech/music - One dimensional signals
Why CNN?

Why CNN?
- Visual Hierarchy: layering
- Spatial locality: Convolution
- Translational Invariance: Pooling
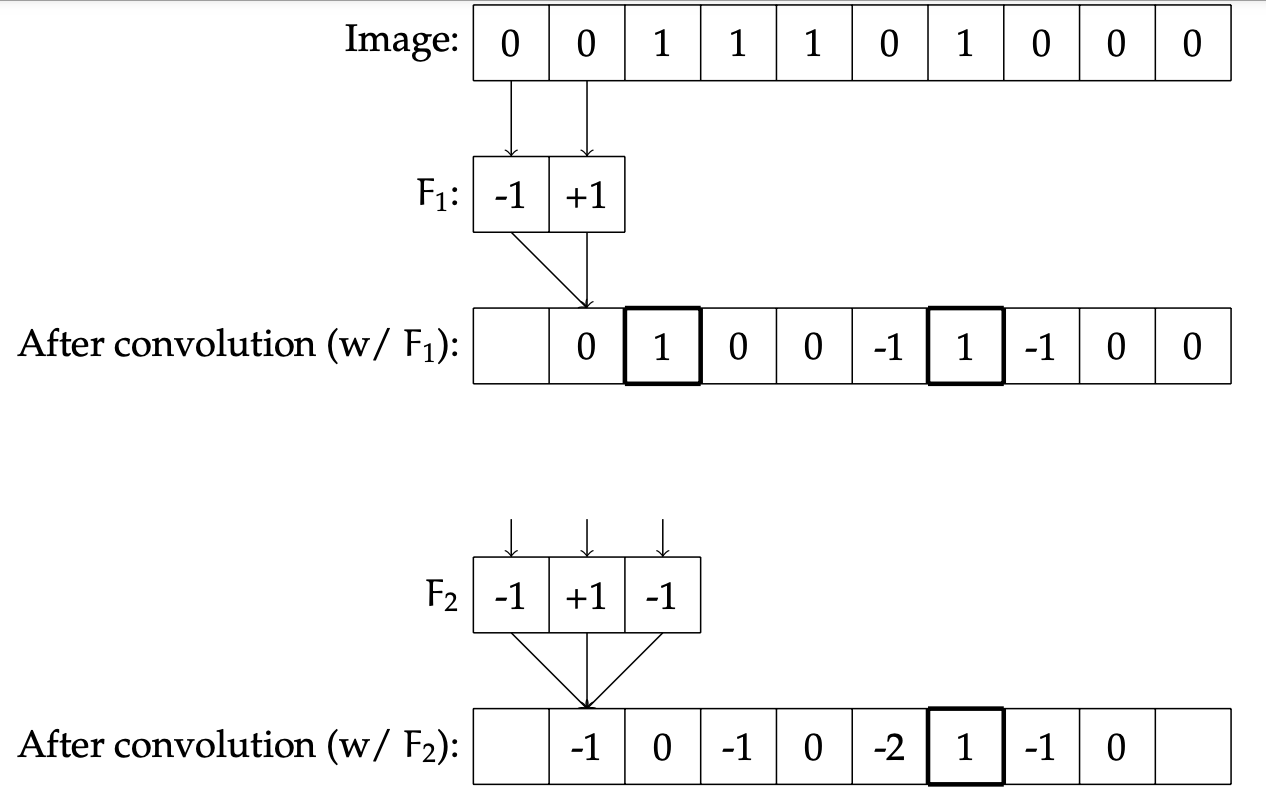
Filters: Convolution
An image filter is a function that takes in a local spatial neighborhood of pixel values and detects the presence of some pattern in that data.
Let \(X\) be the original image, of size \(d\); then pixel \(i\) of the output image is specified by:
\[ Y_i = F \cdot (X_{i-1}, X_i) \] This process of applying the filter to the image to create a new image is called convolution.
Filters: Convolution
Multiple Filters: Detect different features in one layer
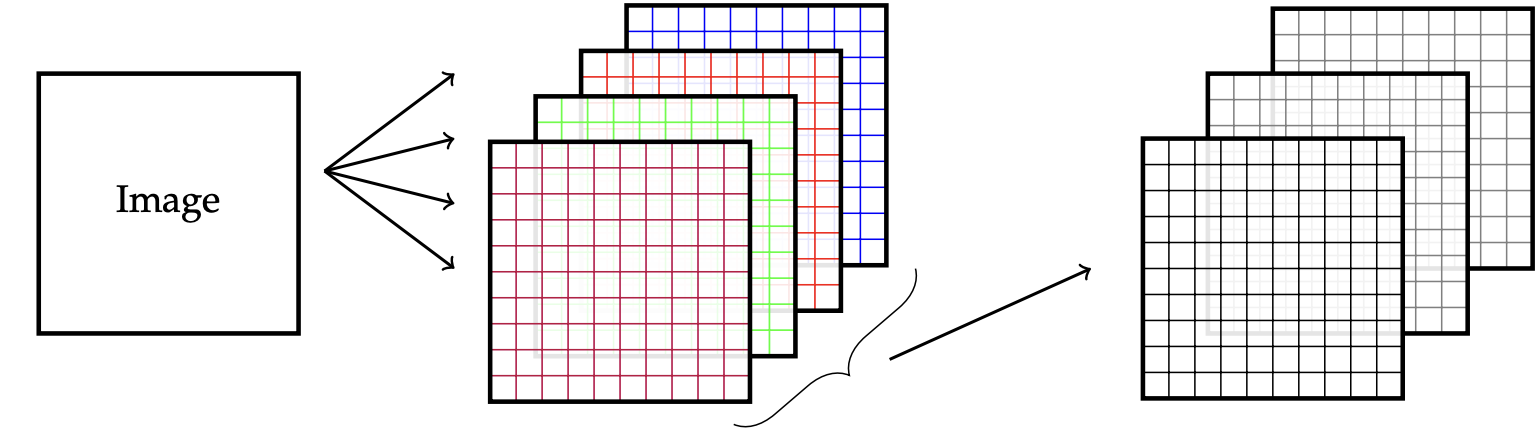
- If there are \(m\) filters applied to the original image, the size of the output is \(m\) images ( \(m\) channels).
Example: Layering convolutions
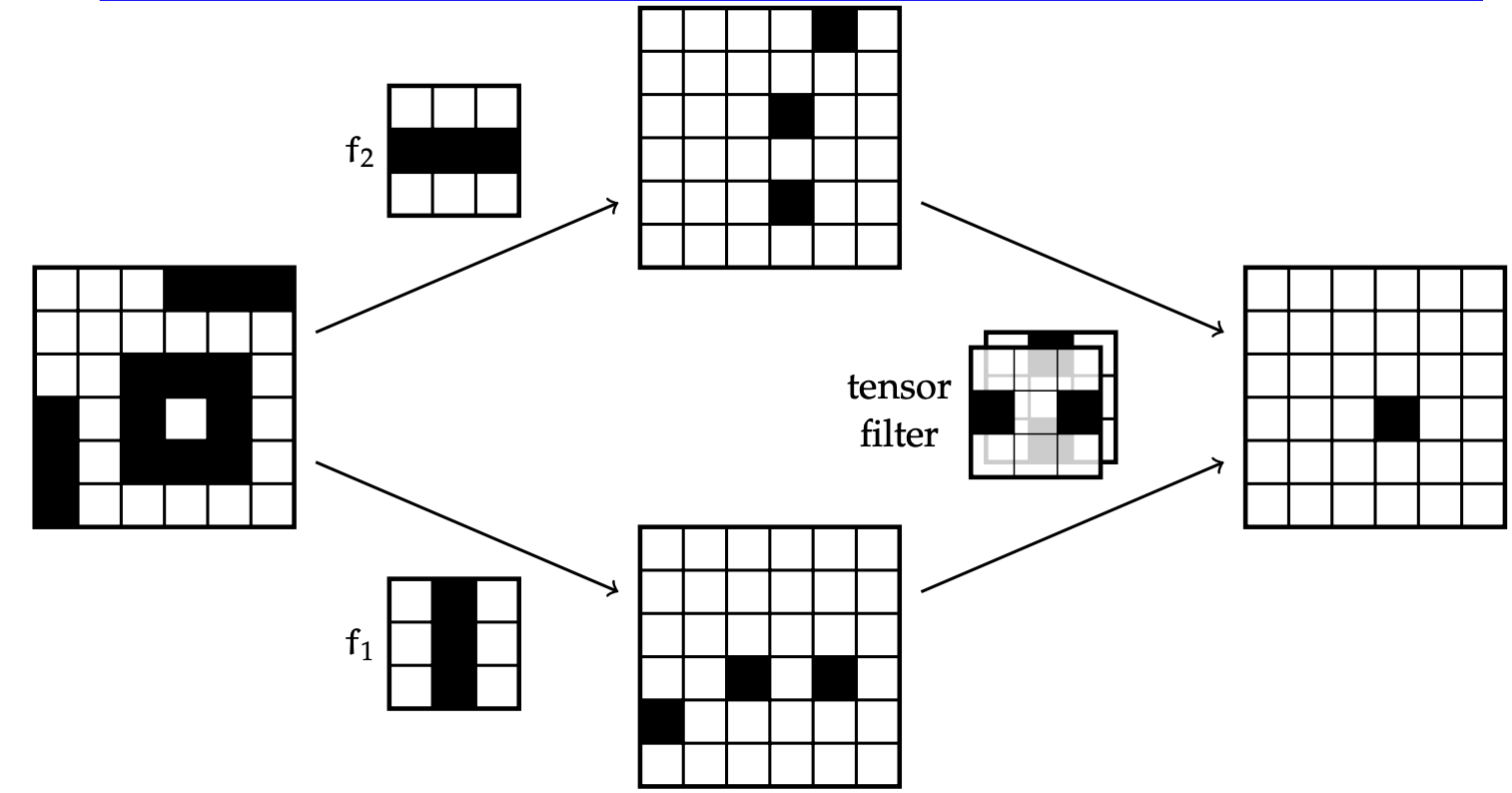
Convolutional Layer Parameters
Number of filters: \(m_l\)
Size of one filter: \(k_l \times k_l \times m_{l-1} + 1 \text{ (for the bias value for this one filter).}\)
Stride \(s_l\): The stride determines the spacing at which the filter is applied to the image.
Input tensor size: \(n_{l-1} \times n_{l-1} \times m_{l-1}\)
Padding \(p_l\): Refers to the number of extra pixels (typically with value \(0\)) added around the edges of the input.
Max-Pooling
Max-pooling is a simple yet powerful operation in CNNs:
- Reduces computational complexity.
- Enhances translational invariance.
- Emphasizes prominent features.
- Improves generalization by reducing overfitting.
Max-pooling

- Set stride \(s^l\)
- Set size \(k^l \times k^l\) (\(k^l \geq s^l\)).
Typical Architecture
Here is the form of a typical convolutional network:
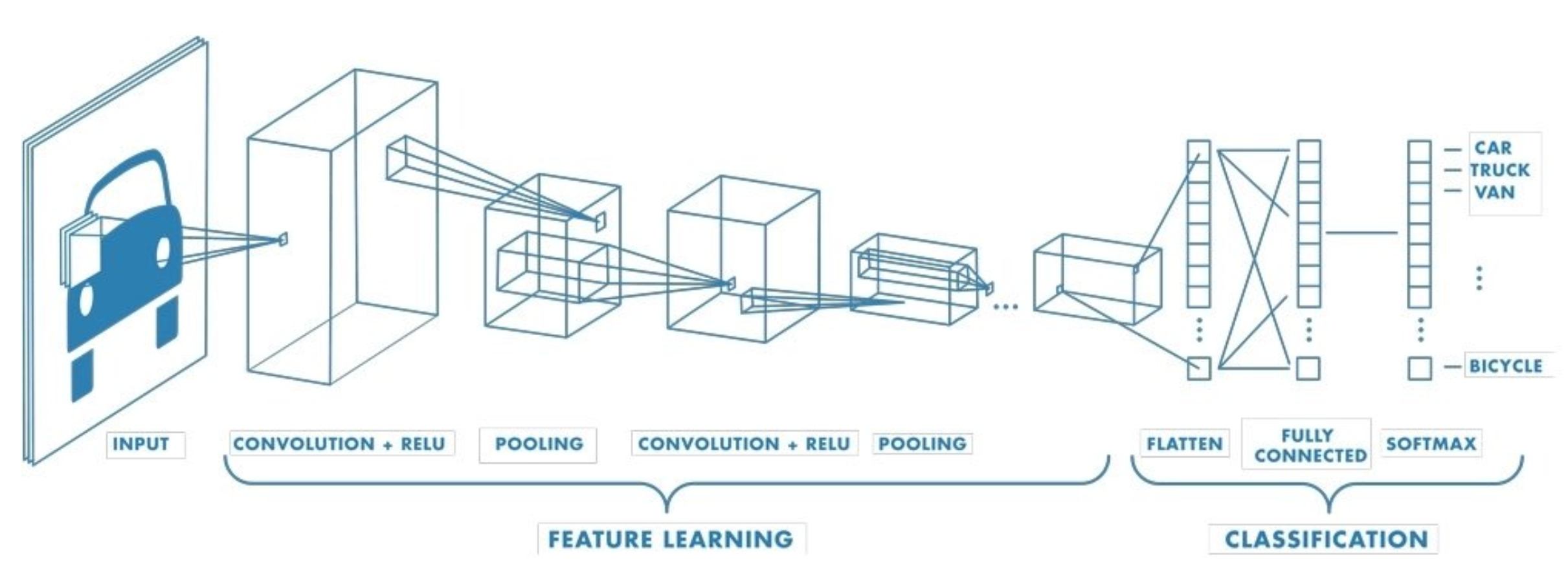
Typical Architecture
- Initial layers: Feature extraction.
- After each filter layer there is generally a ReLU layer; there maybe be multiple filter/ReLU layers and max-pooling layers.
- Final layers: Clasification/Regression
- Once the output is down to a relatively small size, there is typically a last fully connected layer, leading into an activation function such as softmax that produces the final output.
Back-propagation: A simple example
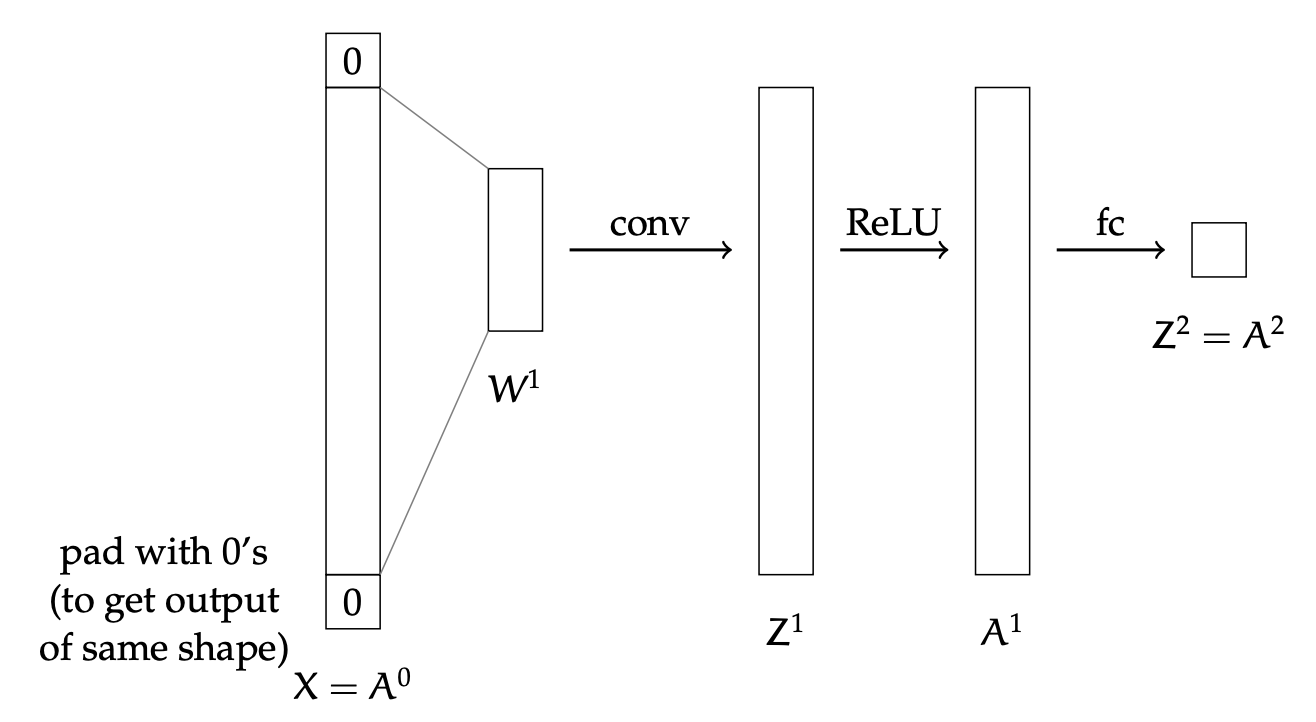
Back-propagation: A simple example